Severe Maternal Morbidity
Municipality-Level Variation in Severe Maternal Morbidity and Association With Municipal Expenditures in New Jersey
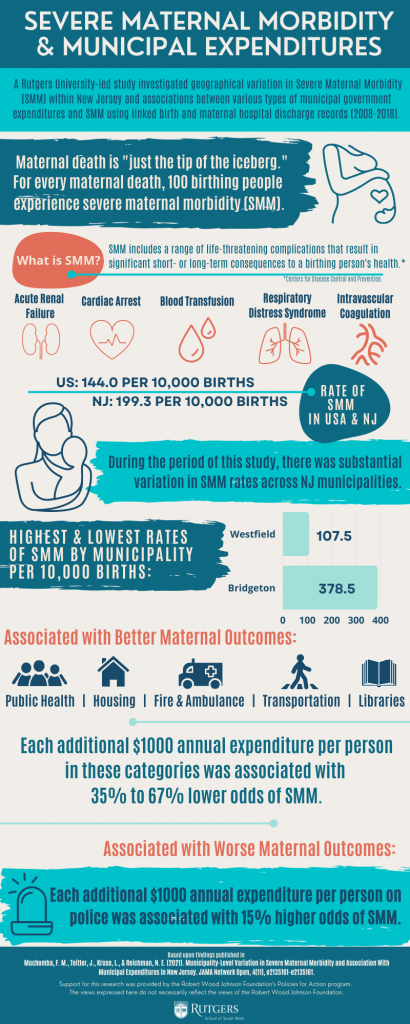
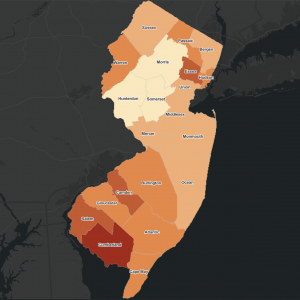
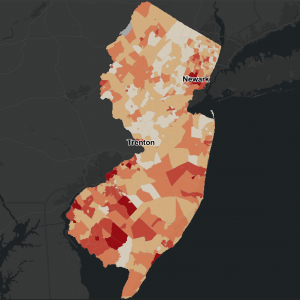
This study, based on 1 million births from 2008 to 2018 in New Jersey, found that municipal expenditures on fire and ambulance, transportation, health, housing, and libraries were negatively associated with severe maternal morbidity, whereas expenditures on police were associated with higher odds of severe maternal morbidity.
For more information
- Infographic [PDF] [PNG] [JPG]
- Press Release [Local Budgets May Cause Severe Consequences for Maternal Outcomes in New Jersey]
- Published Article [Municipality-Level Variation in Severe Maternal Morbidity and Association With Municipal Expenditures in New Jersey]
∗New Study∗
Association Between Housing Affordability and Severe Maternal Morbidity
This study found that higher municipal rental housing costs were significantly associated with greater odds of severe maternal morbidity. The availability of publicly supported affordable housing attenuated the associations. Among mothers with less than a high school education, the risk of severe maternal morbidity was 8.0% lower for each additional $1000 annual municipal-level housing subsidy per person with an income lower than poverty level, which translated to a 20.7% lower educational disparity in severe maternal morbidity.
For more information
- Press Release [New Jersey Women Living in Costly Rental Areas More Likely to Experience Labor and Delivery Complications]
- Published Article [Association Between Housing Affordability and Severe Maternal Morbidity]