Cryptomeria Scale (Aspidiotus cryptomeriae ‘Kuwana’)
GDD Window (base 50): 533-820
Overview:
- Beware of the scale hiding beneath a transparent cover!
- Overwinter as immature nymphs in a waxy covering on needles
- Looks like a fried egg (nymphs and adult females are yellow, and produce a white wax coating around them) & flat in appearance
- Crawlers are lemon yellow in color
- Crawler periods last 4 or more weeks
- Two crawler generations per year, in June and August
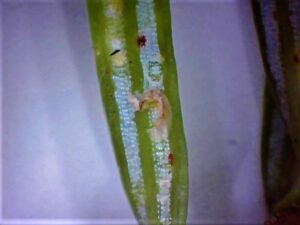
- Causes mottling or chlorotic banding appearance on upper needle surfaces & causes premature needle drop
- Monitor lower branches losing their green coloring
- Damage happens and spreads quickly
- Host plants: conifers (hemlocks, pines, firs) True firs in Christmas tree farms are most susceptible (rarely on cryptomeria)
Management:
Cultural Practices:
- Natural predators: brown lacewings, green lacewings, lady beetles, & Parasitoid wasps
- Prevent dusty conditions
- Reduce plant stress
- Dispose of heavily infested plants
Materials:
- Contact insecticides:
- Carbamates [1A]: carbaryl
- Pyrethroids [3A]: –thrins
- Organophosphates [1B]: acephate (translaminar), malathion
- Considerations:
- Will harm non-target species
- Timing is essential in controlling armored scales (target crawler stage before waxy covering forms)
- Systemic insecticides:
- Neonicotinoids [4A]: dinotefuran, acetamiprid, thiamethoxam
- Tetronic acids [23}: spirotetramat
Biorationals:
- Insecticidal soaps and Horticultural oils
- Neem oil
- Insect growth regulators:
- Pyriproxyfen [7A]
- Buprofezin [16]


Disclaimer – Materials do not cover all possible control scenarios and are intended for licensed professionals. Tradenames do not imply endorsement and are used as examples. You must strictly follow the label for each compound prior to use. Rutgers is not responsible form is used materials or damages thereof. The label is the law. Labels will provide detailed information on use and restrictions. Additionally, application intervals, compatibility, surfactant use, PHI, PPE, important and other key information is described in detail. Always discuss treatments with your local agents. Note: Neonicotinoids can only be legally applied in commercial agriculture settings by licensed applicators. Guidelines and recommendations made in this presentation are specific to the state of New Jersey.
