Indian Wax Scale (Ceroplastes ceriferus)
GDD Window (base 50): 700-1200
Overview:
- Soft-bodied insects covered in white, waxy secretions, and found on branches and stems
- Adult females are rounded, hemispherical, white, and up to ¼” in diameter – resemble a wad of gum
- Males do not exist (Parthenogenetic)
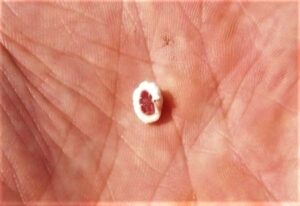
- Crawlers are rusty-red
- All life stages can be found on trigs and branches & not foliage
- One generation per year
- Overwinter on bark as adults = (dormant oils less effective)
- Sticky honeydew and sooty mold on plant surfaces
- Yellowing and premature leaf drop, decreased plant vigor, branch dieback
- Host plants: 62 plant families
- Evergreen shrubs including Inkberry holly, blue hollies, Japanese holly, Chinese holly, boxwood, Euonymus
- Deciduous shrubs including Spirea, flowering quince, barberry, Japanese maple
Management:
Cultural Practices:
- Natural predators: parasitic wasps, predatory beetles, ladybeetles, lacewings
- Prune infested branches
- Remove by hand when possible
- Prevent plant stress
- Give plants ample spacing
- Avoid over fertilizing
- Syringing
Materials:
- Contact insecticides:
- Pyrethroids [3]: –thrins
- Carbamates [1A]: carbaryl
- Systemic insecticides:
- Neonicotinoids [4A]: imidacloprid, dinotefuran, acetamiprid
- Abamectin [6]
- Considerations:
- Will harm non-target species
- Target sprays during crawler stage
Biorationals:
- Horticultural oil (not dormant)
- Insecticidal soap
- Insect Growth Regulators:
- Pyriproxifen [7C]
- Buprofezin [16]
Resources:
Some Key Soft Scale Pests in the Landscape – PPA
Landscape Pest Notes for Late June 2023 – PPA


Disclaimer – Materials do not cover all possible control scenarios and are intended for licensed professionals. Tradenames do not imply endorsement and are used as examples. You must strictly follow the label for each compound prior to use. Rutgers is not responsible form is used materials or damages thereof. The label is the law. Labels will provide detailed information on use and restrictions. Additionally, application intervals, compatibility, surfactant use, PHI, PPE, important and other key information is described in detail. Always discuss treatments with your local agents. Note: Neonicotinoids can only be legally applied in commercial agriculture settings by licensed applicators. Guidelines and recommendations made in this presentation are specific to the state of New Jersey.
