Japanese Beetle (Popillia japonica)
GDD Window (base 50): 1029-2154
Overview:
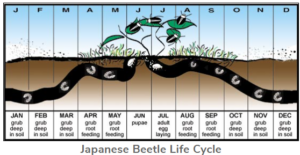
- Mate, then feed and lay eggs for six weeks
- Adults appear on hosts from late June to early August
- Attracted to plant-feeding damage and often cluster on one particular plant
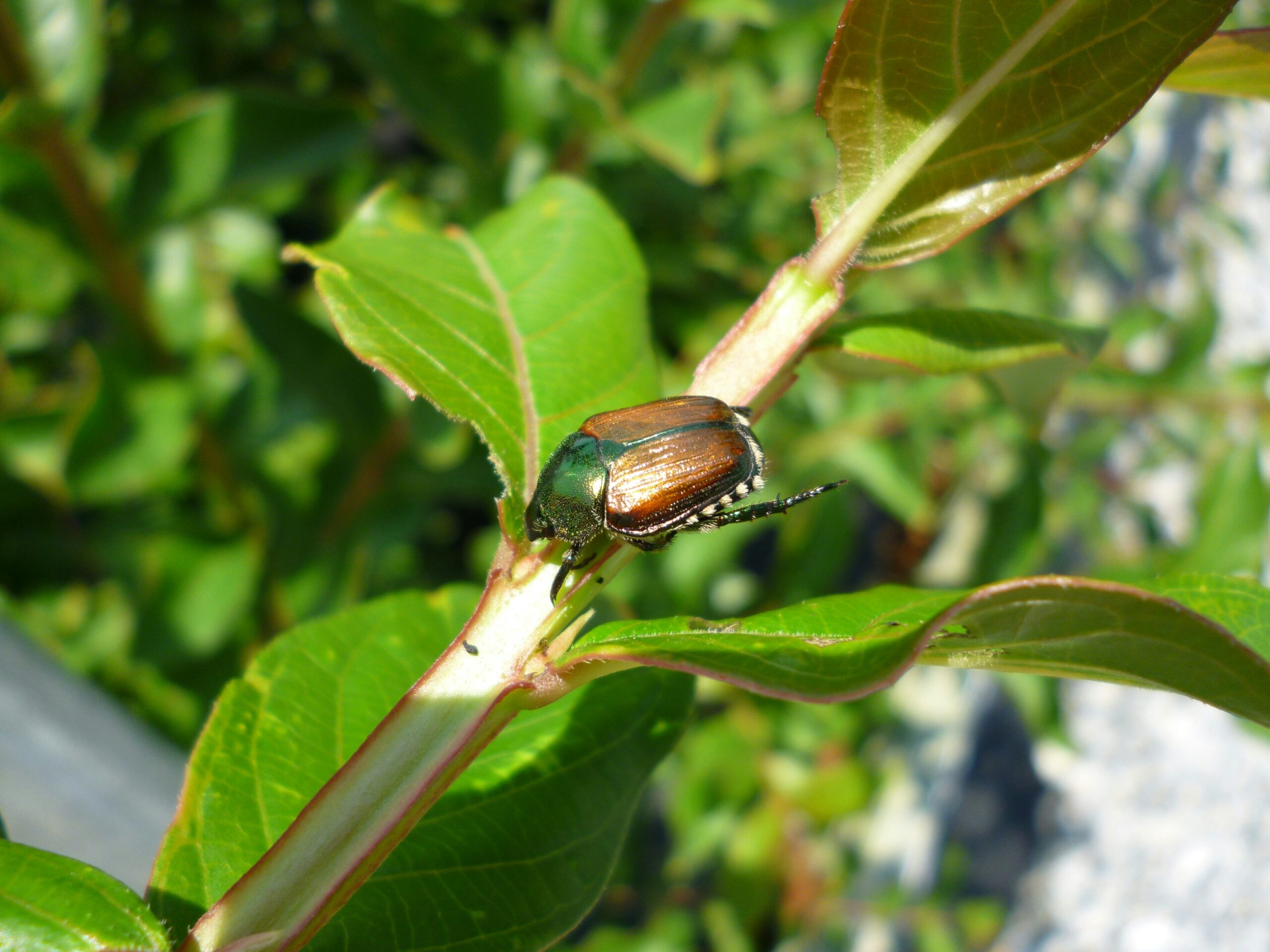
- Adults are ½” long with a metallic green body and coppery-brown wing covers, white tufts of hair along the sides of their abdomens
- Larvae are white with brown heads, C-shaped, and feed on plant roots
- One-year long life cycle
- Eggs are laid in the soil
- Cause skeletonized leaves, brown or pale patches in lawns
- Beetles are mostly present on sunny days
- Can lead to increased bird activity locally
- Host plants: roses, grapes, linden & birch trees, and fruit trees (apples, cherries, peaches) & crabapples
- Larvae feed on roots of turfgrass and ornamentals
Management:
Cultural Practices:
- Natural predators: birds, (starlings, robins, crows), mammals (raccoons, skunks), ants, spiders, assassin bugs, parasitoids (Tiphia vernalis, Istocheta aldrichi)
- Companion planting: catnip, chives, garlic
- Adults are sluggish on cool/rainy days or early in the morning, and can be handpicked or knocked into a drop cloth
- Choose plants that are less susceptible (boxwood, dogwood, magnolias)
- Take care of your lawn by mowing, fertilizing, and watering to prevent grubs
- Reduce plant stress
- Use pheromone traps
Materials:
- Contact insecticides:
- Carbamates [1A]: carbaryl
- Pyrethroids [3]: –thrins
- Systemic insecticides:
- Neonicotinoids [4A]: Acetamiprid, imidacloprid, dinotefuran
- Diamides [28]: Chlorantraniliprole
- Organophosphate [1B]: acephate
- Considerations:
- Most will harm non-target species
Biorationals:
- Horticultural oil / Soaps
- Neem oil
- Azadirachtin [UN]
- Milky spore bacteria (targets grubs)
- Diamides [28]: Chlorantraniliprole
Resources:
Japanese Beetle Quarantine – RU Entomology
Japanese Beetle Suppression – RU Entomology
Landscape Pest Notes for July 2023 – PPA



Disclaimer – Materials do not cover all possible control scenarios and are intended for licensed professionals. Tradenames do not imply endorsement and are used as examples. You must strictly follow the label for each compound prior to use. Rutgers is not responsible form is used materials or damages thereof. The label is the law. Labels will provide detailed information on use and restrictions. Additionally, application intervals, compatibility, surfactant use, PHI, PPE, important and other key information is described in detail. Always discuss treatments with your local agents. Note: Neonicotinoids can only be legally applied in commercial agriculture settings by licensed applicators. Guidelines and recommendations made in this presentation are specific to the state of New Jersey.
