Development & Implementation of Efficient Numerical & High-performance Computational Techniques
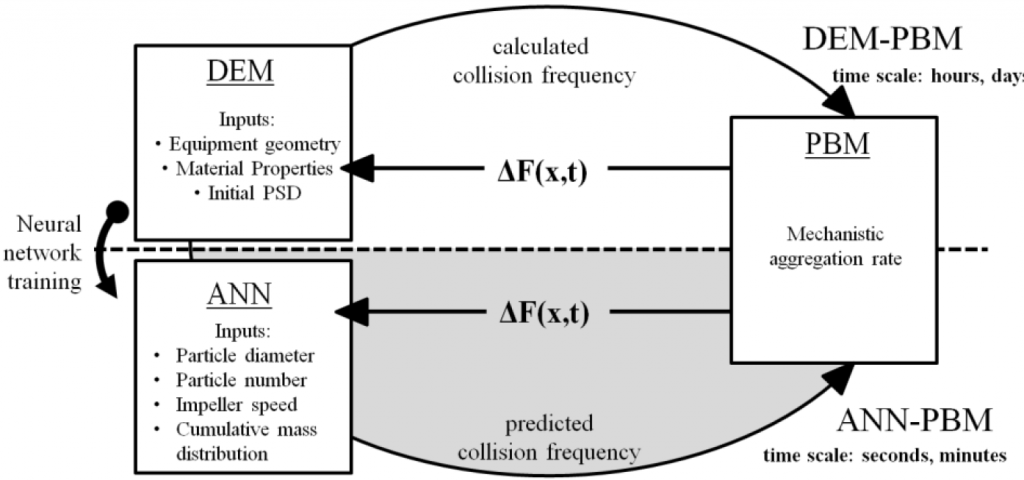
Here, we seek to develop better numerical techniques and model reduction techniques to solve complex process models (e.g. PBM and PBM-DEM ) with reduced simulation times whilst maintaining high accuracy. We also work on the massive parallelization of population balance models using high performance and distributed computing techniques.
Cell-average Technique
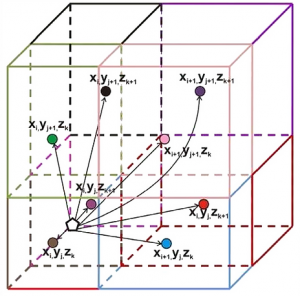
Parallel Computing
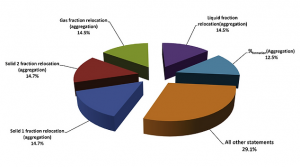
Model Order Reduction

-
- D. Barrasso, A. Tamrakar, R. Ramachandran. A reduced order PBM-ANN model of a multi-scale PBM-DEM description of a wet granulation process. Chemical Engineering Science, 119, 319-329, 2014.
- A. Chaudhury, I. Oseledets, R. Ramachandran, A computationally efficient technique for the solution of multi-dimensional PBMs of granulation via tensor decomposition, Computers & Chemical Engineering, 61, 234-244, 2013.
- Anuj V. Prakash, Anwesha Chaudhury, and Rohit Ramachandran, “Parallel Simulation of Population Balance Model-Based Particulate Processes Using Multicore CPUs and GPUs,” Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, vol. 2013, Article ID 475478, 16 pages, 2013.
- A.V. Prakash, A. Chaudhury, D. Barrasso and R. Ramachandran. Simulation of population balance model-based particulate processes via parallel and distributed computing. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 91(7),1259–1271, 2013.
- A. Chaudhury, A. Kapadia, D. Barrasso, A.V. Prakash and R. Ramachandran. An Extended Cell-average Technique for Multi-Dimensional Population Balance Models describing Aggregation and Breakage. Advanced Powder Technology, 24(6), 962-971, 2013.
- D. Barrasso and R. Ramachandran. A comparison of model order reduction techniques for a four-dimensional population balance model describing multi-component wet granulation processes. Chemical Engineering Science, 80, 380-392, 2012.