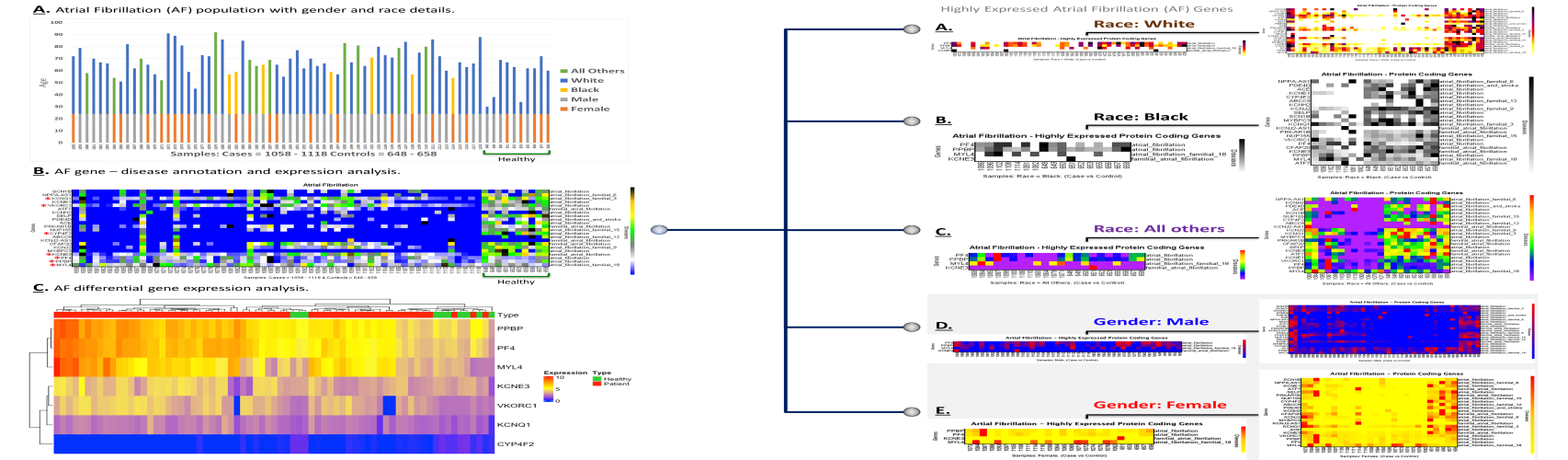
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) disease is defined as high-frequency excitation of the atrium, resulting in both dyssynchronous atrial contraction and irregularity of ventricular excitation. AF, includes risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, smoking and sedentary lifestyle. It is exasperated in older male individual of European Ancestry. Previous studies have shown that both heart failure (HF) and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) contribute to increasing the risk of AF. In this study, we investigated genes responsible for AF with sub-disease groups by implementing transcriptomic analysis. This study has been conducted as a continuation of our CVD with HF genes research and was performed with 61 CVD patients with patient samples (Sample IDs: 1058-1118) and wild type samples (Control IDs: 648-658). When grouped by gender and race, there are; 40 males and 21 females, 42 Whites, 7 Blacks (Blacks or African Americans), 1 Asian, 1 Decline to Answer, and 8 NA (Table 1). Blood samples were taken via peripheral blood and used for RNA extraction and an Illumina NovaSeq 6000-S4 was used to assess the RNA samples. Efficient data management system (PROMIS-LCR) and data extraction, transfer, and loader system (ETL), which were created by us, have been used in previous work for patient recruitment and consent tracking as well as dealing with the all-omics data, respectively. Our findings demonstrate that we have investigated and reported four highly expressed genes and their association with AF and its relative diseases; PF4: atrial fibrillation; PPBP: atrial fibrillation; MYL4: atrial fibrillation familial 18; KCNE3: familial atrial fibrillation, similar in all groups (Black-African American race, White race, All Others race, Female, Male). Moreover, when we compared the genes associated with HF from our previous CVD/HF study with those associated with AF, we discovered that two genes (ACE and MYBPC3) were associated with both diseases (HF and AF). The findings are valuable for future research studies and personalized therapy and provide information in the field of precision medicine.
Publication:
– Berber, A., Abdelhalim, H., Zeeshan, S., Vadapalli, S., von-Oehsen, B., Yanamala, N., Sengupta, P., & Ahmed, Z. (2022). RNA-seq driven expression analysis to investigate Cardiovascular disease genes with associated phenotypes among Atrial Fibrillation patients. Clinical and Translational Medicine. PMID: 35875838. (Wiley)