PK-PD Modeling of Biofilm Infections
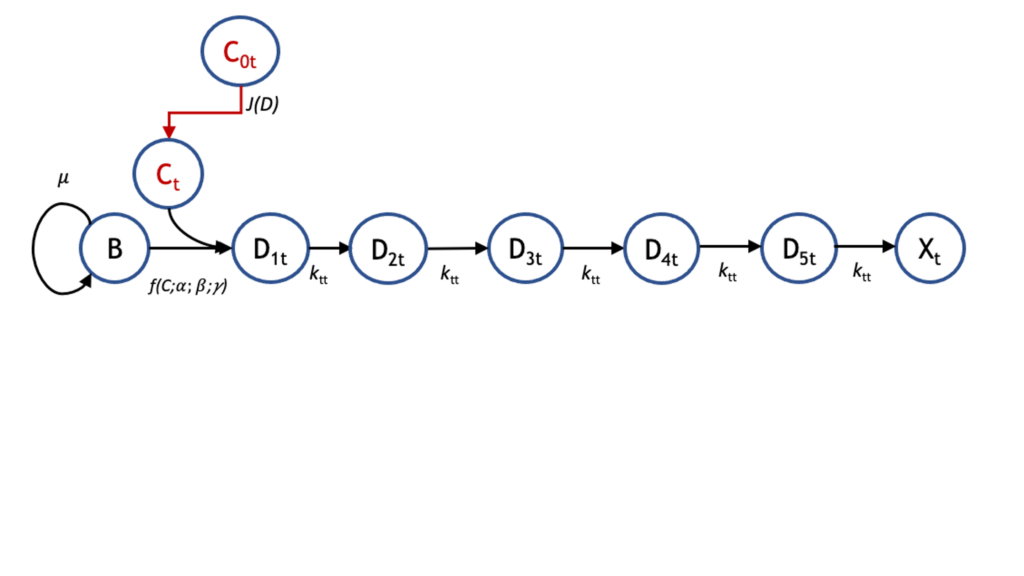
Accurate pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) models of biofilm treatment could be used to guide formulation and administration strategies to better control bacterial lung infections. To this end, we developed a detailed pharmacodynamic model of P. aeruginosa treatment with the front-line antibiotics, tobramycin and colistin, and validated it on a detailed dataset of killing dynamics. A compartmental model structure was developed in which the key features are the diffusion of the drug through a boundary layer to the bacteria, concentration-dependent interactions with bacteria, and the passage of the bacteria through successive transit states before death. Current efforts are focused on coupling this PD model with a PK model that describes distribution to and from the lungs to provide an integrated PK-PD description relevant to treatment of bacterial lung infections. This can be used to optimize administration and timing protocols for single- and multiple-drug regimens to eradicate emerging and persistent infections.